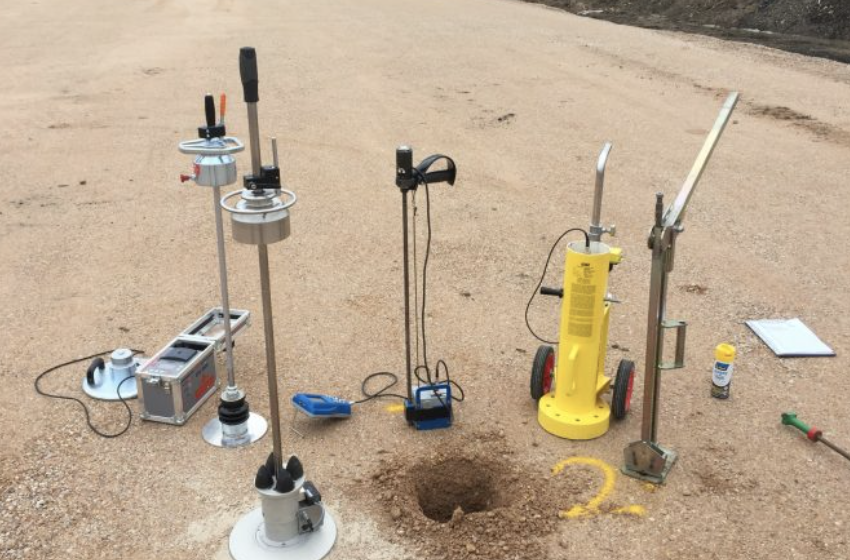
Which Soil Density Test Method to Use?
Choosing the right soil density testing method can significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of construction projects. Whether it’s building roads, foundations, or embankments, selecting the correct density test method ensures optimal soil compaction and long-term stability. Here’s a clear guide to help you determine which soil density test method is best suited for your project.
What Are the Most Common Soil Density Test Methods?

Several standard methods exist for measuring soil density, each with strengths and suitable applications:
- Sand Cone Test1: Uses sand displacement to measure in-place soil density.
- Nuclear Density Gauge2: Measures density through radiation to provide rapid results.
- Core Cutter Method3: Uses cylindrical cutters to extract and weigh soil samples.
- Water Displacement Method: Measures density by displacing water with soil.
| Method | Speed | Accuracy | Cost Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Cone | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Nuclear Gauge | Fast | High to Moderate | High (initial cost) |
| Core Cutter | Slow | High | Low |
| Water Displacement | Slow | Moderate | Low |
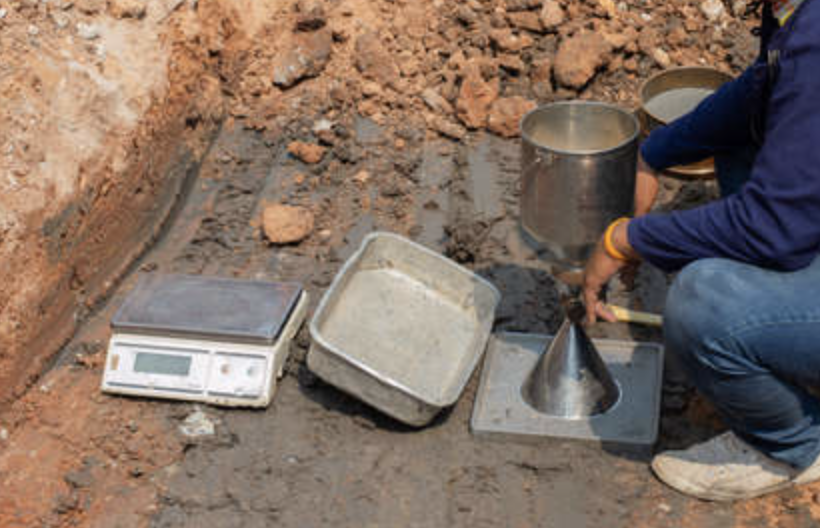
When Should You Use the Sand Cone Test?

The sand cone test is a traditional and highly reliable method ideal for small-scale projects requiring accurate results.
- Ideal situations include:
- Small areas or individual tests
- Projects with strict accuracy standards
- Locations inaccessible to heavier equipment
The sand cone test, while slower than the nuclear gauge method, offers precise and trusted results, especially for quality control4 in critical structures.
Is the Nuclear Density Gauge Always Accurate?
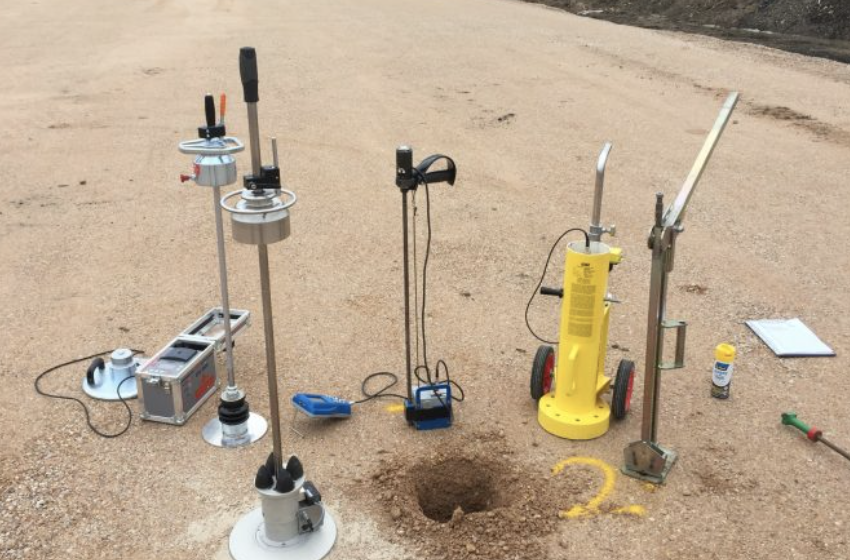

The nuclear density gauge provides quick readings and is convenient, but accuracy can vary based on site conditions.
- Factors influencing accuracy:
- Soil moisture content
- Calibration errors
- Surface roughness and debris
| Advantage | Limitation |
|---|---|
| Rapid test results | Sensitive to calibration errors5 |
| Portable and convenient | Requires trained operators |
| Good for large projects | Regulatory compliance needed |
Regular calibration and trained personnel are essential for obtaining reliable results from nuclear density gauges.
Which Method Works Best for Field vs Lab Testing?
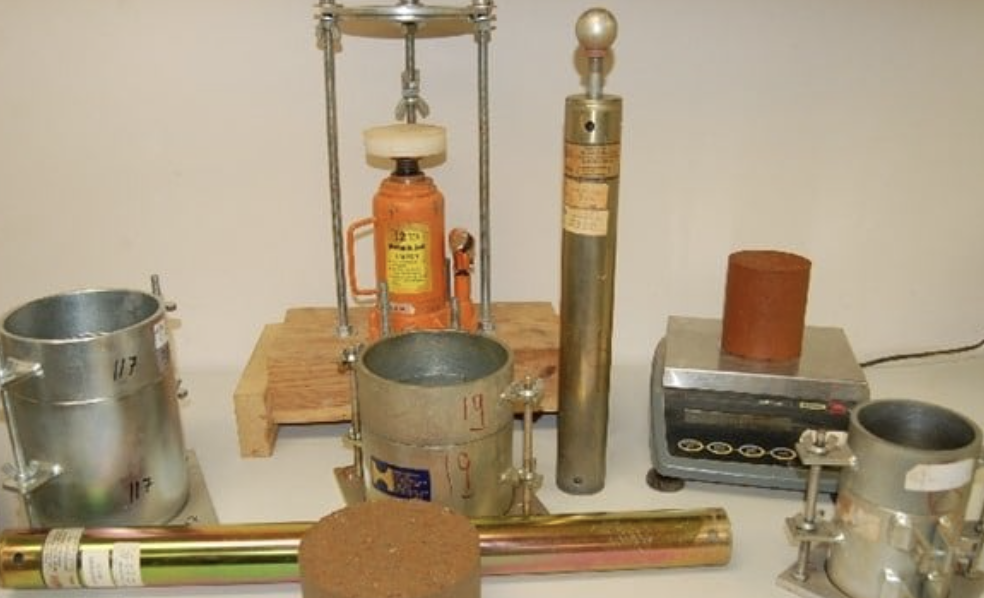

Choosing between field and laboratory methods depends on your project’s requirements:
-
- Preferred methods: Sand Cone, Nuclear Density Gauge
- Applications: On-site compaction quality control, roadway construction, embankments.
-
- Preferred methods: Core Cutter, Water Displacement
- Applications: Detailed soil studies, confirming field data, design specifications.
| Location | Recommended Method(s) | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Field | Sand Cone, Nuclear Density Gauge | Fast, practical, and reliable |
| Lab | Core Cutter, Water Displacement | High accuracy, controlled conditions |
Conclusion
Selecting the correct soil density test method is crucial to ensure construction stability and reliability. Consider project size, accuracy requirements, and site conditions to choose the most suitable method, whether it’s the traditional sand cone, rapid nuclear gauge, or precise laboratory methods.
-
Explore this link to understand the Sand Cone Test’s methodology and applications in soil density measurement. ↩
-
Learn about the technology behind Nuclear Density Gauges and their advantages in soil density testing. ↩
-
Discover the Core Cutter Method’s process and its effectiveness in obtaining accurate soil density measurements. ↩
-
Learn about effective quality control practices that can enhance the reliability of construction projects and ensure safety. ↩
-
Exploring calibration errors will help you ensure accurate measurements and improve the reliability of your results. ↩
-
Explore the benefits of Field Testing methods to understand their practical applications in construction projects. ↩
-
Learn about the advantages of Laboratory Testing methods for accurate soil analysis and design specifications. ↩