How Does a Laboratory Jaw Crusher Excel in Geological Sample Preparation?
In the field of geoscience, accurate sample preparation1 is the gateway to meaningful data. Whether analyzing rock, ore, or mineral cores, precise size reduction is essential before chemical or structural testing. That’s where the laboratory jaw crusher2 shines—bridging the gap between field-collected specimens and refined lab results.
Geological Sample Characteristics Requiring Crushing
Geological samples come in diverse forms3—igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks4, mineralized ores5, and weathered fragments. Each presents unique challenges for preparation.
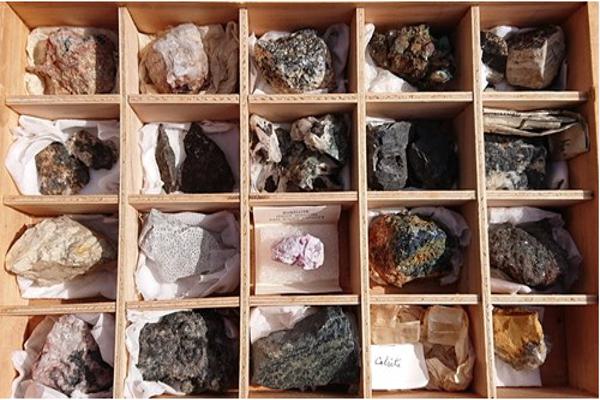

Common Sample Properties:
- Hardness: Mohs scale 5–9, requiring high compression force
- Irregular shape: Demands a wide feed opening
- Heterogeneity: Uniform reduction ensures representative analysis
| Sample Type | Typical Hardness | Reason for Crushing |
|---|---|---|
| Granite | 6–7 | Mineral composition analysis |
| Bauxite | 1–3 | Al content & grain size study |
| Iron ore | 5–7 | Metallurgical and grade testing |
| Schist | 4–5 | Structural and petrographic work |
To preserve data quality, consistent particle size and minimal contamination during crushing are non-negotiables.
Unique Features of Laboratory Jaw Crushers for Geological Samples
Unlike large industrial crushers, lab jaw crushers6 are tailored for sample control7, safety, and precision. Their compact design8 and adjustability make them ideal for geologists.
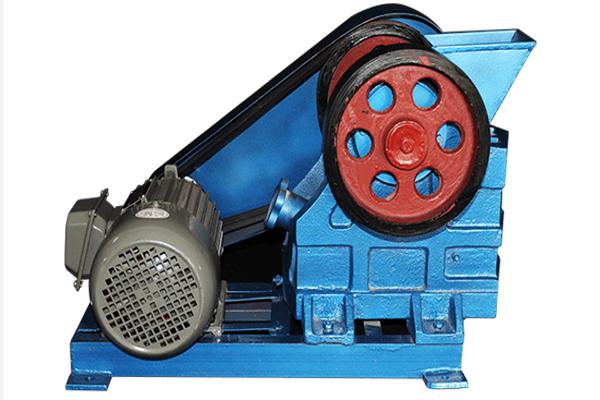

Why They’re Preferred:
- Adjustable output size: From ~0.5 mm to 10 mm
- High-strength jaw plates: Handle quartz, basalt, and iron ore
- Low sample loss: Design reduces dust and fines
- Contamination-free options: Tungsten carbide or ceramic jaws for trace element labs
| Característica | Geological Testing Benefit |
|---|---|
| Precise gap adjustment | Controls particle size distribution |
| Compact & benchtop ready | Fits limited lab space |
| Dust-reducing enclosures | Safe for heavy mineral samples |
| Hardened jaw materials | Prevents sample-metal interference |
Laboratory jaw crushers make repeatable, analytical-grade crushing possible even in high-throughput academic or industrial labs.
Step-by-Step Process of Using Crushers in Geological Labs
Proper technique ensures that raw geological samples are transformed into representative, analyzable fractions without introducing bias.

Standard Operating Procedure:
- Initial inspection – Remove surface contaminants and label samples.
- Jaw spacing setup – Select desired final particle size (e.g., 2 mm).
- Feed sample – Slowly introduce rock fragments to avoid overload.
- Collect and sieve – Use a sieve stack to isolate required size fractions.
- Clean between samples – Avoid cross-contamination using brushes or air.
| Paso | Importance |
|---|---|
| Size uniformity | Ensures representative sub-sampling |
| Cleaning procedure | Prevents trace metal carryover |
| Slow feeding | Avoids uneven or excessive grinding |
When followed diligently, this method enables quantitative trace analysis and reproducible petrographic evaluations.
Case Studies of Precise Mineral Analysis Enabled by Crushers
Numerous academic and industry labs rely on jaw crushers for data integrity. Here are real-world examples:

Case 1: Trace Element Analysis in Volcanic Basalts
At a geochemistry lab, butted basalt samples were crushed using a tungsten-carbide jaw crusher. Final product: 2 mm fraction, later pulverized for ICP-MS. No contamination detected from jaw surfaces.
Case 2: Gold Content Testing in Quartz Veins
A mining company in Nevada prepared drill cores with a lab jaw crusher. The precise 3 mm particle sizing allowed for gravity separation tests, helping to assess the viability of a low-yield deposit.
Case 3: Rare Earth Element Mapping
In China, samples from clay-hosted REE deposits were prepped with ceramic-jawed crushers to avoid heavy metal contamination. The result: high-resolution XRF scans with clean baseline readings.
| Study Focus | Jaw Crusher Contribution |
|---|---|
| Gold assay accuracy | Preserved mineralogy without smearing |
| Trace element purity | Non-reactive jaws ensured clean signals |
| Particle size control | Enabled optimized downstream processing |
Conclusión
For anyone working with rock, ore, or mineral samples, a laboratory jaw crusher is not just a convenience—it’s a necessity. By offering precise size control, low contamination, and robust performance, it plays a vital role in transforming geological samples into scientific insight.
-
Understanding accurate sample preparation is crucial for obtaining reliable data in geoscience research. ↩
-
Exploring how a laboratory jaw crusher operates can enhance your knowledge of sample preparation techniques in geoscience. ↩
-
Exploring this resource will provide insights into the various types of geological samples and their significance in geology. ↩
-
Understanding these rock types is crucial for anyone interested in geology, as they form the foundation of geological studies. ↩
-
This link will help you learn about mineralized ores, their formation, and their economic significance in the field of geology. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how lab jaw crushers enhance precision and safety in geological sample analysis. ↩
-
Learn about the importance of sample control in geology and how it affects research outcomes. ↩
-
Discover the benefits of compact design in lab equipment, especially for space-constrained environments. ↩