What Exactly Is a Laboratory Jaw Crusher and How Does It Work?
In material science, mining, and geotechnical engineering, precision is everything—especially when it comes to sample preparation. That’s where the laboratory jaw crusher1 comes in. Compact, powerful, and built for precision, it plays a critical role in reducing bulk samples to analyzable sizes. But what is it, and how does it work? Let’s explore its structure, principle, performance specs, and how it stacks up against industrial crushers.
Defining the Structure and Components of a Laboratory Jaw Crusher
At its core, a laboratory jaw crusher is a scaled-down version of the heavy-duty jaw crushers used in mining and quarrying—but built for benchtop or floor-mounted use in controlled lab environments.
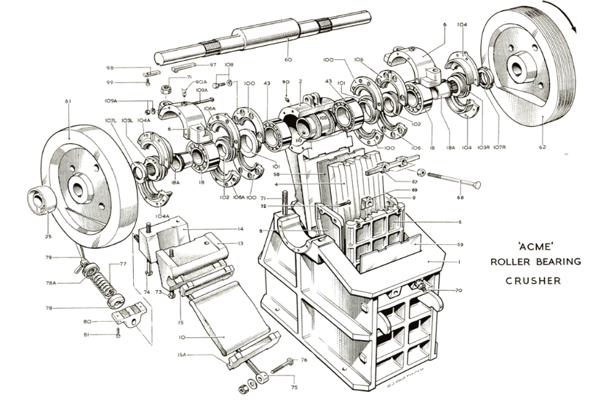
Core Components:
- Fixed Jaw Plate: Rigid side of the crushing chamber.
- Moveable Jaw Plate: Oscillates to apply compressive force.
- Jaw Gap Adjustment Mechanism2: Allows precise control of output size.
- Feed Hopper3: Guides bulk material into the jaws.
- Drive Motor4: Powers the movement (usually electric).
- Safety Guard and Collection Pan: Ensures safe and clean operation.
| Componente | Función |
|---|---|
| Crushing chamber | Holds and reduces sample size |
| Adjustment knob | Sets the final particle size |
| Hardened jaws | Ensure longevity and crush strength |
| Collection drawer | Captures crushed product cleanly |
The design is compact and optimized for precision, repeatability, and ease of cleaning—perfect for laboratory settings.
The Fundamental Working Principle Behind Jaw Crusher Operation
A lab jaw crusher operates on the principle of compressive force5—crushing materials between two plates: one fixed and one that moves in a reciprocating motion.
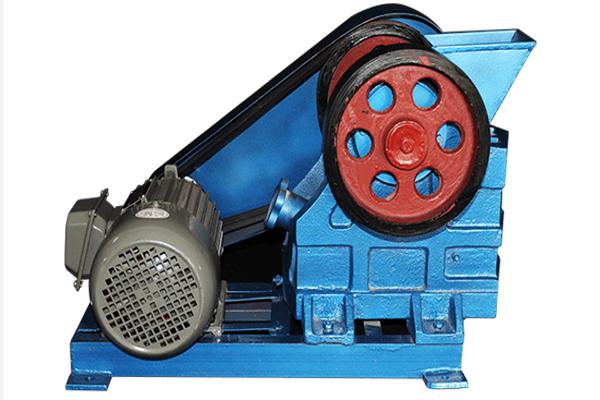

Cómo funciona:
- Feed material (rocks, ores, minerals) enters the chamber via the hopper.
- The moveable jaw6 is powered to move back and forth.
- As the jaws converge, the material is compressed and fractured7.
- The crushed product exits through the bottom when it reaches the desired size.
| Stage of Operation | Result |
|---|---|
| Jaw closure | Sample is fractured and reduced |
| Jaw opening | Material falls further into the chamber |
| Final ejection | Particles pass through adjusted gap |
This cyclic motion allows the crusher to gradually reduce particle size while controlling uniformity and avoiding over-grinding.
Key Technical Parameters that Define Performance
Not all lab jaw crushers are created equal. Performance is defined by a few key technical parameters, which dictate crushing capacity, product quality, and material compatibility.

Main Parameters to Consider:
- Feed size: Max particle diameter (often 50–100 mm)
- Output size: Adjustable (typically 0.5–20 mm)
- Throughput: Ranges from 100 kg/h to 1,000+ kg/h
- Jaw material: Hardened steel, tungsten carbide, ceramic
- Motor power: Typically 1.5–3.0 kW
| Parámetro | Typical Range in Lab Crushers |
|---|---|
| Input size | Up to 100 mm |
| Output size | 0.5–10 mm adjustable |
| Throughput capacity | 150–1,000 kg/h |
| Jaw hardness | HRC 60+ for wear resistance |
These specs determine how well the machine handles various materials—from soft limestones to hard ferrous ores.
Comparing Laboratory Jaw Crushers with Industrial-Scale Models
While they share the same basic principles, lab jaw crushers and industrial crushers differ significantly in size, power, and intended application.
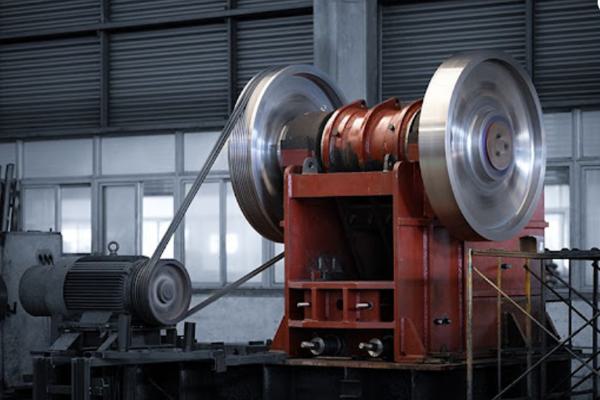

Key Differences:
| Característica | Laboratory Jaw Crusher | Industrial Jaw Crusher |
|---|---|---|
| Size and footprint | Benchtop or small floor unit | Large-scale, fixed installations |
| Feed capacity | 50–1,000 kg/h | Several tons per hour |
| Output size | Finer, highly adjustable | Coarse primary reduction |
| Material compatibility | High-purity options for trace analysis | Heavy-duty mining and aggregate crushing |
| Typical use | Research, testing, mineral analysis | Mining, cement, construction |
Lab crushers are best for controlled, small-batch processing, while industrial crushers dominate in volume-driven environments.
Conclusión
A laboratory jaw crusher is a precision instrument engineered to break down tough materials into test-ready fragments. From the fixed and moving jaws to its customizable output and high durability, it supports accurate, efficient, and contamination-free sample preparation in materials testing labs around the world. Whether you’re analyzing ore, rock, or alloy—this small yet powerful device helps unlock big insights.
-
Understanding the laboratory jaw crusher’s function and design is crucial for effective sample preparation in various fields. ↩
-
Understanding the Jaw Gap Adjustment Mechanism is crucial for optimizing output size in crushing operations. Explore this link for detailed insights. ↩
-
The Feed Hopper plays a vital role in guiding materials into the crushing chamber. Learn more about its function and importance. ↩
-
The Drive Motor is essential for the operation of crushers. Discover the different types and their impact on performance. ↩
-
Understanding compressive force is crucial for grasping how lab jaw crushers effectively crush materials. ↩
-
Exploring the role of the moveable jaw will enhance your knowledge of the crushing process and its efficiency. ↩
-
Learning about compression and fracturing will provide insights into material behavior during crushing operations. ↩