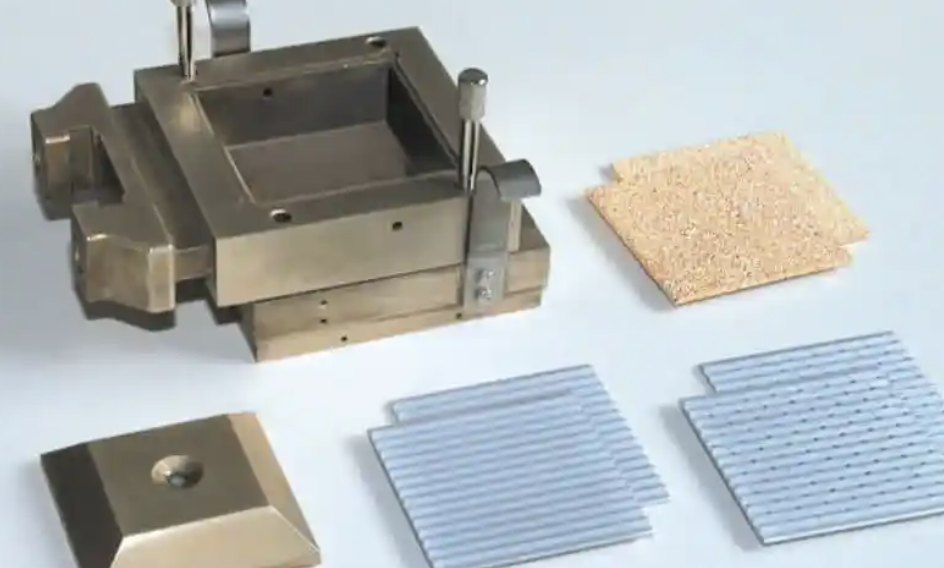
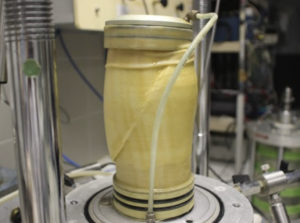
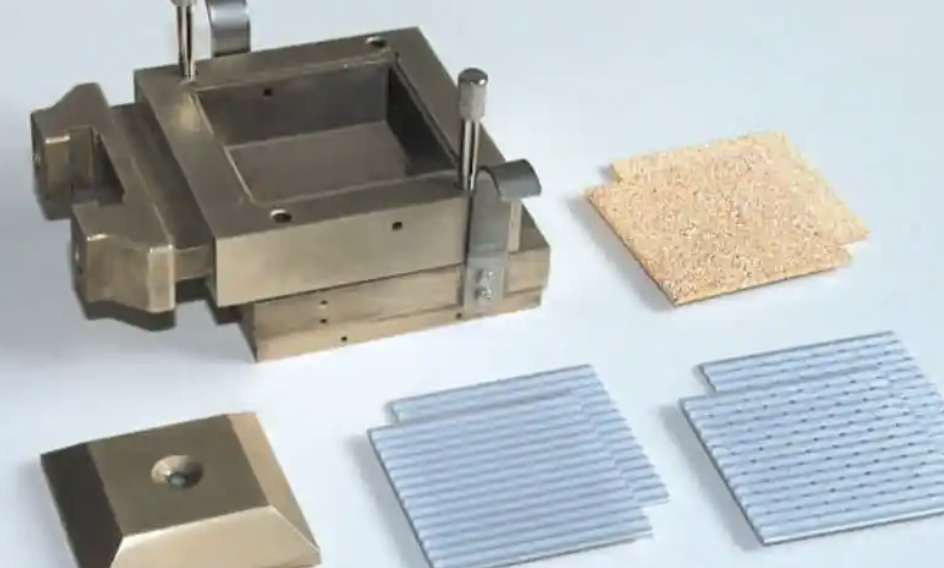
What is a Direct Soil Shear Test?
A direct soil shear test is a laboratory method used to measure the shear strength of soils. It helps engineers determine the stability of slopes, foundations, and retaining walls. By understanding how soil behaves under shear stress, safer and more effective engineering decisions can be made.
What Principle Does the Direct Shear Test Follow?
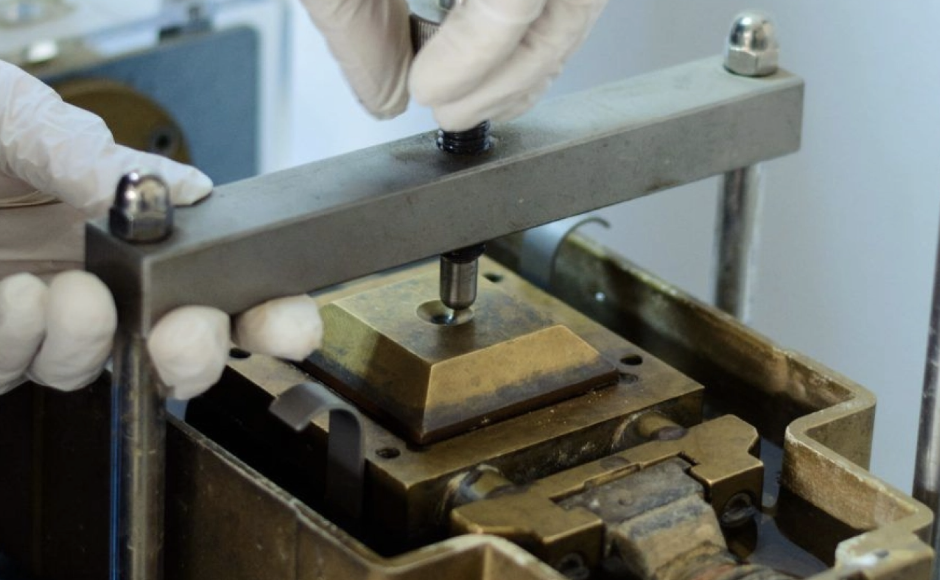

The direct shear test works by applying horizontal shear force to a soil sample confined under a constant vertical (normal) load. The test continues until the soil fails, providing crucial data on:
- Shear strength1: Resistance to shearing forces.
- Cohesion (c)2: The internal bonding force between soil particles.
- Friction angle (φ)3: Resistance caused by particle friction.
These parameters form the basis of soil stability analysis.
How Is the Soil Sample Prepared for Testing?

Proper sample preparation ensures accurate results:
- Sieving: Soil is typically passed through a No. 4 sieve (4.75 mm) to remove large particles.
- Moisture adjustment: Soil moisture content4 is adjusted to match field conditions.
- Placement in shear box: Soil is evenly compacted into a horizontally split shear box5, carefully avoiding air voids.
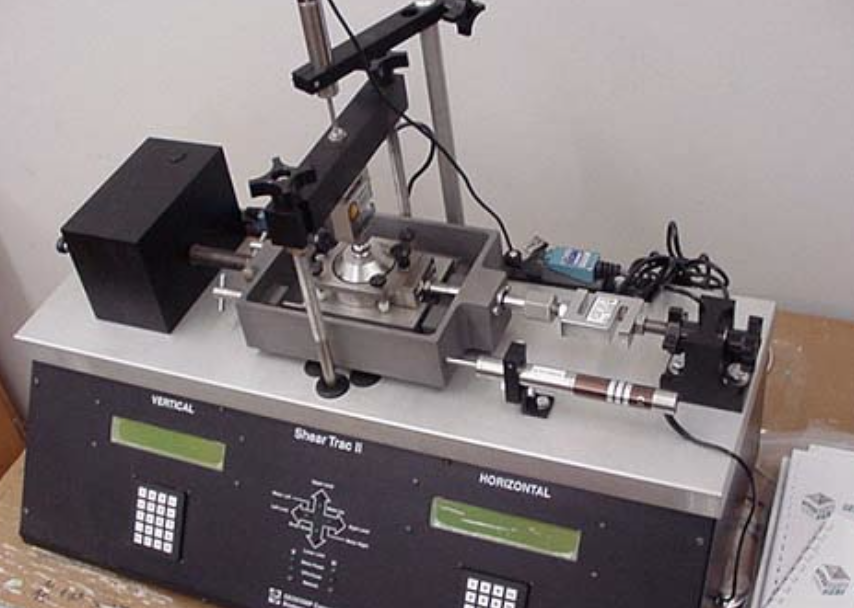
What Equipment Is Used in a Direct Shear Test?
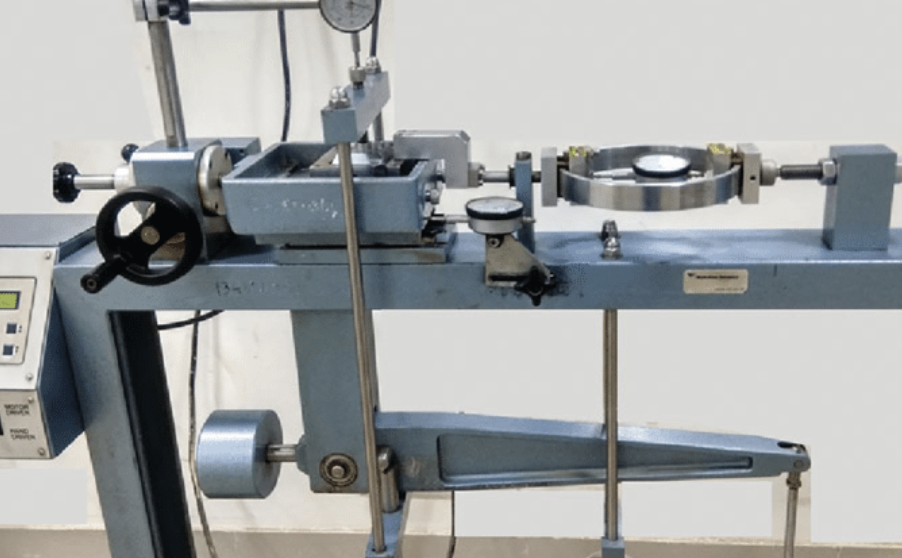
The essential equipment includes:
| Equipo | Función |
|---|---|
| Shear Box | Holds the soil sample and allows shear deformation |
| Loading Frame | Applies vertical normal load |
| Horizontal Loader | Applies controlled horizontal shear force |
| Dial Gauges/Sensors | Measure soil deformation and applied forces |
What Can the Test Results Tell Us?
Direct shear test results provide key information:
- Peak shear stress6: Maximum resistance before soil failure.
- Residual shear stress7: Long-term strength after significant displacement.
- Mohr-Coulomb parameters (c and φ)8: Used in stability analyses and foundation designs.
| Result | Engineering Significance |
|---|---|
| Cohesión (c) | Determines stability of cohesive soils |
| Ángulo de fricción (φ) | Indicates stability of granular soils |
| Peak shear strength | Guides initial design and safety factors |
| Residual strength | Crucial for assessing long-term slope stability |
Conclusión
The direct shear test is vital for evaluating soil strength, ensuring stability in geotechnical engineering projects. Accurate sample preparation, reliable equipment, and careful result interpretation are essential to making sound engineering decisions.
-
Understanding shear strength is essential for evaluating soil stability and designing safe structures. ↩
-
Cohesion plays a vital role in soil stability; exploring this can enhance your knowledge of soil mechanics. ↩
-
The friction angle is crucial for predicting soil behavior under load; learning more can improve your engineering skills. ↩
-
Understanding soil moisture content is crucial for accurate testing and analysis in various fields, including agriculture and construction. ↩
-
Learning about the shear box’s function can provide insights into soil behavior under stress, essential for engineering applications. ↩
-
Understanding peak shear stress is essential for evaluating soil stability and designing safe structures. ↩
-
Exploring residual shear stress helps in assessing long-term soil behavior and slope stability, crucial for engineering projects. ↩
-
Learning about Mohr-Coulomb parameters enhances your knowledge of soil mechanics, vital for foundation design and stability assessments. ↩