Triaxial latex membranes are essential in geotechnical testing, but how exactly do they work? Let’s dive into their importance and function.
Triaxial latex membranes are used to simulate pressure conditions in soil tests. These membranes ensure accurate readings by maintaining controlled environments, crucial for soil analysis.
The triaxial test is key to understanding soil behavior under stress. Let’s explore how latex membranes play a role in this.
How does a triaxial test work?
A triaxial test measures soil’s response to pressure in three directions, crucial for determining its strength and stability. But how does it all come together?
Triaxial tests apply pressure to a soil sample from all sides to simulate real-world conditions, helping engineers understand the material’s behavior under load.

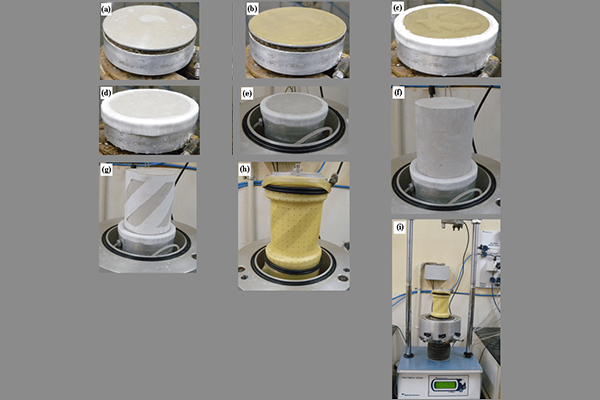
The process of a triaxial test1 involves placing a cylindrical soil sample in a chamber, which is then surrounded by a latex membrane. The chamber is filled with water or air, and pressure is applied to the sample. The soil is subjected to various stress levels, allowing scientists to observe how it behaves under different conditions. This process helps determine soil properties like shear strength2, which are vital for designing structures like bridges, tunnels, and roads.
Latex membranes play a critical role in these tests. They act as a barrier, preventing water or air from directly contacting the soil, ensuring the sample’s integrity. These membranes are flexible, yet durable, allowing them to withstand high pressure while ensuring accurate measurements.
The triaxial test1 process is crucial for understanding how soils will behave under different pressures and environmental conditions. Engineers and scientists rely on these tests to design safer structures and better foundations.
What is latex membrane?
Latex membrane is a flexible, elastic material that’s widely used in geotechnical and construction testing. But what makes it the material of choice?
Latex membranes are used for their strength, flexibility, and ability to resist deformation under pressure. They provide an airtight seal for soil samples during testing.

Latex membranes are made from natural or synthetic rubber and have high elasticity. This makes them perfect for use in triaxial tests, where flexibility and durability are key. In these tests, the membrane prevents contamination and ensures that the pressure is applied correctly to the soil. Without latex membranes, the results could be skewed, as external factors could interfere with the test.
The membrane’s properties, including its stretchability, allow it to conform perfectly to the shape of the sample, ensuring uniform pressure distribution. This is essential for obtaining accurate results in the triaxial test. Latex membranes can also be designed to specific thicknesses, depending on the needs of the test, further enhancing their adaptability.
In addition to triaxial tests, latex membranes are also used in permeability and consolidation tests3, as they provide the necessary sealing to keep fluids or gases from escaping.
What is the purpose of a triaxial compression test?
The triaxial compression test is one of the most important tests in soil mechanics. But what exactly does it measure?
The triaxial compression test evaluates soil’s shear strength, a key property for understanding how the soil will perform under pressure.

A triaxial compression test4 is essential for assessing the shear strength of soils5. This helps engineers determine how the soil will behave under loading conditions, such as the weight of a building or road. The results of these tests can indicate whether the soil is stable enough to support structures or if it requires further treatment.
In the test, the soil sample is subjected to axial compression while being confined laterally. This allows the tester to measure the maximum stress the soil can withstand before failing, which is a critical factor in construction and engineering projects. By varying the pressure and observing the sample’s response, engineers can also determine the soil’s behavior under different conditions, providing a comprehensive understanding of its stability.
The test is used not only for construction purposes but also for environmental assessments, ensuring that the soil can support structures without risking collapse or shifting under stress.
How to use latex membrane in triaxial test?
Using latex membranes in triaxial tests is essential for ensuring accurate, reliable results. But how do they work in practice?
Latex membranes are carefully placed around the soil sample, forming a seal that allows accurate testing of pressure and stress levels during a triaxial test.

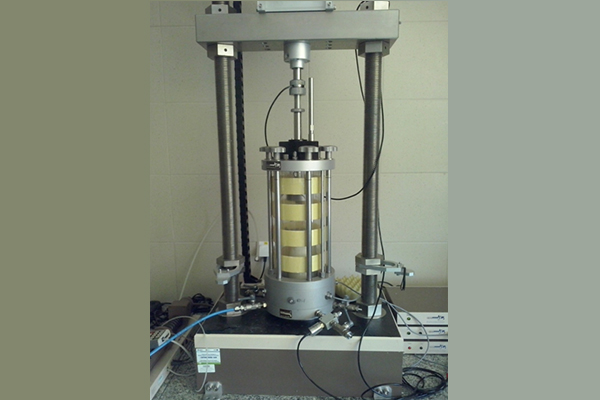
The process of using latex membranes in a triaxial test is quite straightforward, but it requires precision. First, the soil sample is prepared, ensuring it fits snugly within the triaxial testing chamber. The latex membrane is then placed around the sample, and the ends are sealed tightly to prevent leaks. This membrane is essential for applying pressure evenly around the soil sample, simulating the real-world conditions the soil will face.
Once the membrane is in place, the testing chamber is filled with water or air to apply pressure to the sample. The latex membrane prevents the fluid from directly interacting with the soil, ensuring that only the applied pressure is tested. Throughout the process, the pressure inside the chamber6 is carefully controlled to observe how the soil responds to various levels of stress.
Proper membrane installation is critical for the test’s success. If the membrane is not sealed properly, the test results can be compromised, leading to inaccurate data and poor decisions. By using high-quality latex membranes, laboratories can ensure the integrity of their tests and obtain precise, reliable results.
Conclusion
Triaxial latex membranes are vital in soil testing, ensuring pressure is applied correctly and providing reliable data for construction and engineering projects.
-
Understanding the triaxial test is essential for grasping soil behavior under stress, crucial for engineering applications. ↩ ↩
-
Shear strength is a key property in soil mechanics; learning about its measurement can enhance your understanding of soil stability. ↩
-
Discover the significance of these tests in assessing soil behavior, vital for effective engineering solutions and project planning. ↩
-
Understanding the triaxial compression test is crucial for engineers to assess soil stability and ensure safe construction practices. ↩
-
Exploring shear strength helps in understanding soil behavior under load, which is vital for safe engineering and construction. ↩
-
Discover why maintaining pressure is crucial for accurate soil testing and how it affects test outcomes. ↩








2 Responses