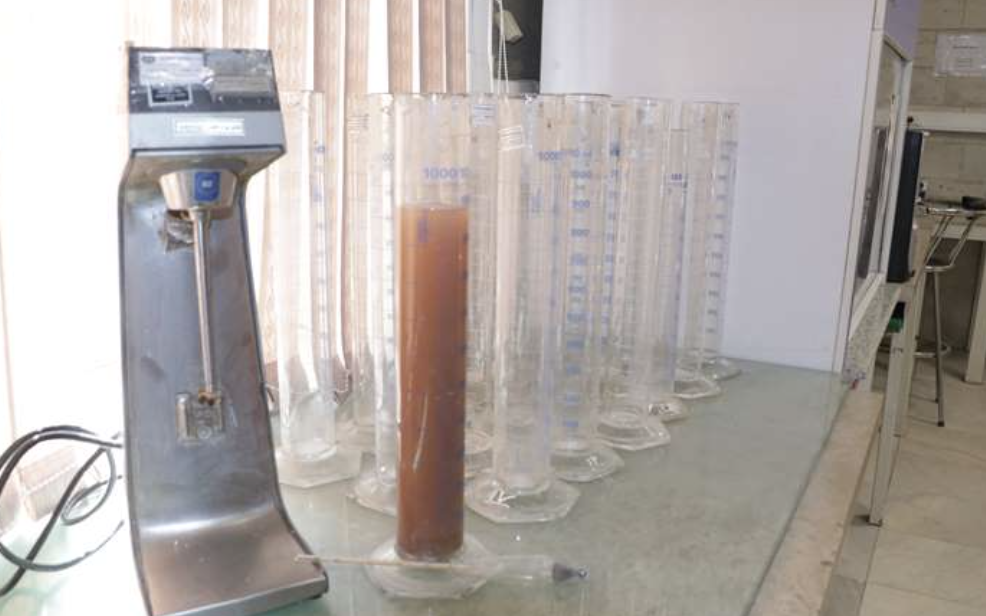
Soil Hydrometer Testing: Sedimentation Method Techniques & Equipments
Soil hydrometer testing is essential for accurately determining particle-size distribution in fine-grained soils. Using sedimentation principles, this test provides critical insights into soil texture, directly influencing soil classification and engineering decisions. Here’s your guide to mastering this important testing technique.
What Is Soil Hydrometer Testing and Why Is It Used?
The soil hydrometer test1 measures how fine soil particles (such as silt and clay) settle in water over time. By observing the sedimentation rate, researchers determine particle size distribution2 in soils.
Key purposes include:
- Classifying soils accurately (USCS and AASHTO systems).
- Designing foundation and pavement layers based on soil type.
- Assessing permeability and drainage characteristics.
Hydrometer tests are particularly effective for soils with significant fine-grained fractions3, offering detailed particle size data that sieve analysis alone cannot provide.
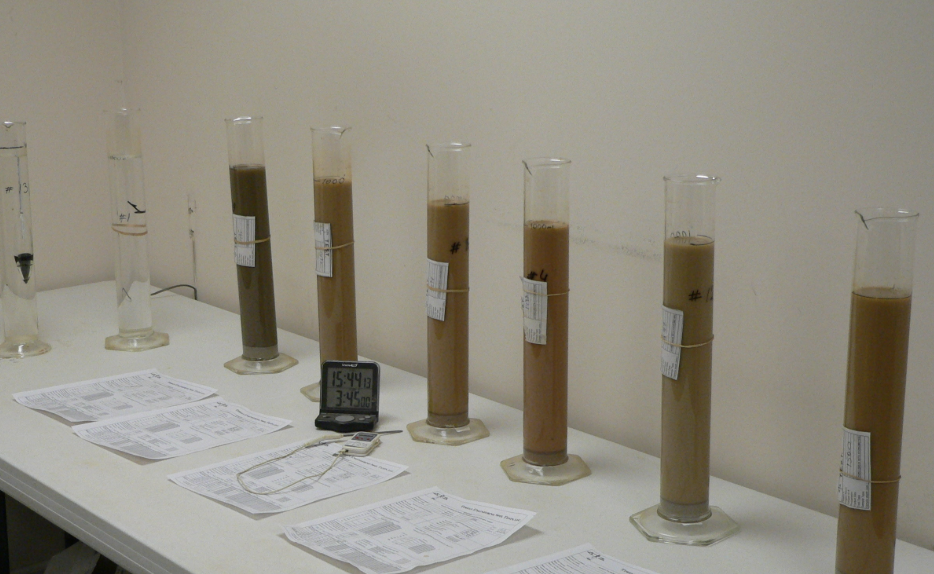

What Equipment Is Required for Sedimentation Testing?
Proper equipment is essential for precise soil hydrometer testing. Your setup typically includes:
| Thiết bị | Mục đích |
|---|---|
| Soil Hydrometer | Measures suspended particle density |
| Sedimentation Cylinder (1000 mL) | Holds soil-water suspension |
| Dispersion Mixer | Ensures uniform soil particle dispersion |
| Thermometer | Monitors temperature during testing |
| Stopwatch or Timer | Records precise sedimentation timing |
| Mechanical Shaker or Stirring Rod | Thoroughly mixes the soil-water suspension |
| Deflocculating Agent (e.g., Sodium Hexametaphosphate) | Prevents particle aggregation |
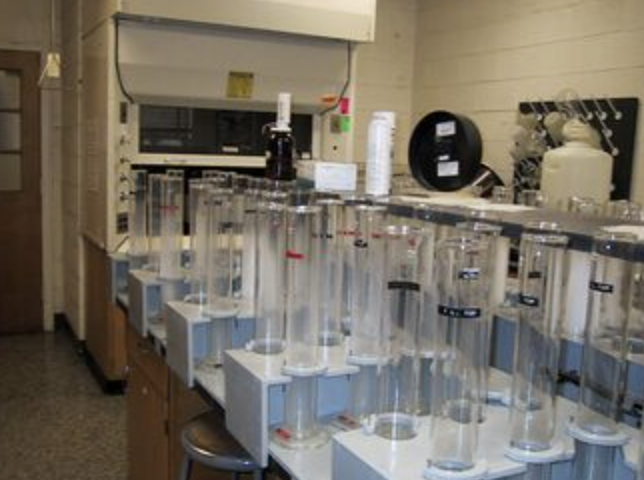

How Is the Test Performed Step-by-Step?
Follow these basic steps for accurate hydrometer testing:
-
Sample Preparation:
- Dry soil, pulverize, and pass through a #10 sieve.
- Weigh approximately 50 grams of fine soil fraction.
-
Dispersion:
- Mix soil sample thoroughly with distilled water and dispersing agent4.
- Allow adequate soaking time (usually overnight).
-
Sedimentation:
- Transfer dispersed sample into sedimentation cylinder and fill to 1000 mL.
- Shake thoroughly or mix to achieve uniform suspension.
-
- Record hydrometer and temperature readings at standardized intervals (e.g., 2 min, 5 min, 15 min, 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hrs, 24 hrs).
-
Calculations and Analysis:
- Correct readings for temperature and meniscus effects.
- Plot particle-size distribution curves6 from corrected data.
What Are the Best Practices for Reliable Results?
Ensure consistency and accuracy by following these best practices:
- Consistent Sample Preparation7: Maintain consistent sample weights and dispersion methods.
- Temperature Control8: Keep sedimentation tests at standardized temperature (typically around 20°C).
- Accurate Timing: Record sedimentation times precisely, as small errors affect results.
- Regular Calibration: Calibrate your hydrometer periodically for accurate readings.
- Multiple Tests: Conduct repeat tests and average results for greater reliability.

Phần kết luận
Soil hydrometer testing is a powerful, precise method to assess particle-size distribution in soils. By carefully selecting the right equipment, strictly following procedural steps, and adhering to best practices, laboratories ensure reliable, accurate data critical for soil classification and engineering applications.
-
Understanding the soil hydrometer test can enhance your knowledge of soil analysis techniques and their applications. ↩
-
Exploring particle size distribution will deepen your insight into soil characteristics and their implications for engineering. ↩
-
Learning about fine-grained fractions can help you understand their role in soil behavior and engineering applications. ↩
-
Exploring the role of dispersing agents can enhance your knowledge of soil sample preparation techniques. ↩
-
Understanding hydrometer readings is crucial for accurate soil analysis, helping you interpret results effectively. ↩
-
Learning to plot these curves is essential for visualizing soil composition and improving agricultural practices. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how consistent sample preparation can enhance the accuracy of your sedimentation tests. ↩
-
Learn about the significance of maintaining standardized temperatures in sedimentation tests for reliable results. ↩