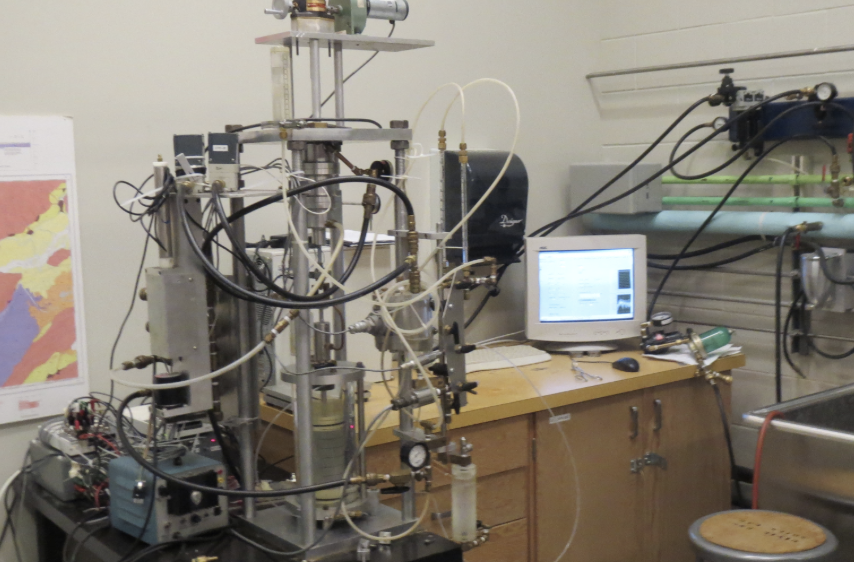
In triaxial shear strength testing, even small errors in latex membrane installation can affect data accuracy. That’s why membrane mounting tools are critical—yet often underestimated—components of any geotechnical lab setup.
Membrane mounting tools play a vital role in ensuring consistent latex membrane placement, protecting specimen integrity, and eliminating variables that compromise triaxial test results.
Let’s explore how they influence test quality and what features to look for.
How Membrane Mounting Tools Impact Test Accuracy
Improperly mounted membranes can lead to specimen damage, trapped air bubbles, or inconsistent confining pressure—all of which distort triaxial test results1.
Using a membrane mounting tool2 ensures a uniform, wrinkle-free fit, which minimizes installation-induced errors and improves test repeatability.
When the membrane is not stretched evenly or is misaligned, the sample may not deform symmetrically under load, affecting the validity of shear strength data.
Tools also help reduce specimen handling, which is especially valuable when testing soft or delicate soils like silts and clays.
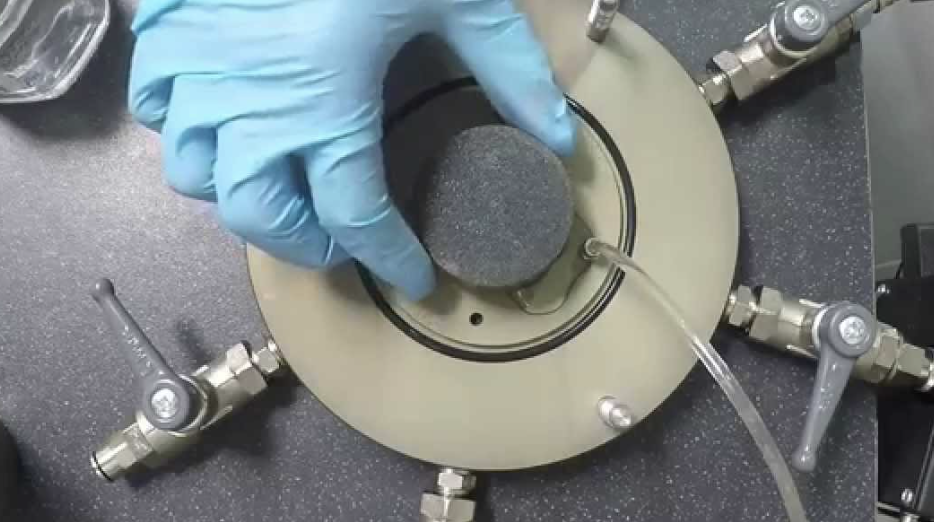

Key Features of Effective Membrane Mounting Tools
Not all mounting tools are created equal. Here’s what makes a tool reliable and lab-ready:
- Smooth, low-friction surface3: Prevents tearing and allows membranes to slide easily
- Tapered or stepped design4: Helps align and stretch the membrane consistently
- Clear acrylic or stainless steel material: Durable and easy to clean
- Compatibility with specimen size: Proper fit avoids overstretching or slack
- Optional vacuum support: For advanced or delicate applications
Look for tools that match your triaxial system’s sample diameters (e.g., 33mm, 50mm, 70mm), and that offer ergonomic ease for technicians.
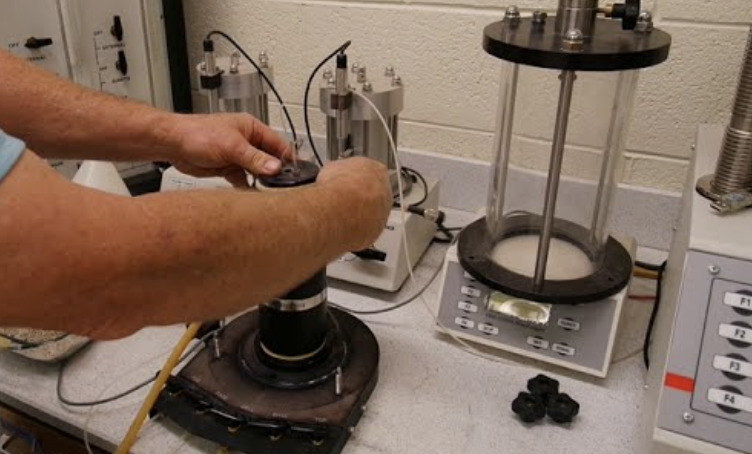

Manual vs. Automated Membrane Mounting: Which is Better for Your Lab?
There are two main types of membrane mounting tools: manual and vacuum-assisted (automated).
| Feature | Manual Tool | Vacuum-Assisted Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low | Medium to High |
| Ease of Use | Moderate | High with training |
| Setup Time | Quick | Longer (requires vacuum) |
| Accuracy for Soft Samples | Depends on user skill | Excellent |
| Ideal For | Routine labs, teaching | Research labs, soft soils |
Manual tools are ideal for most standard applications, offering simplicity and control. Vacuum tools are preferred for high-volume or high-precision testing, where repeatability and reduced handling are essential.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Membrane Mounting Tools
Even with the right tool, mistakes can happen. Here’s how to fix and prevent them:
-
Membrane tears easily5
→ Use lubricant or smoother tool material; ensure membrane isn’t too thin for the sample type. -
Air trapped under the membrane6
→ Slowly roll the membrane and expel air as you go; consider using a vacuum tool. -
Misalignment or slippage
→ Stabilize the sample base and align the membrane evenly at both ends before sealing. -
Tool too tight or too loose
→ Recheck tool diameter—using mismatched tools can stretch or under-tighten the membrane.
Always inspect membranes before and after mounting for leaks or stress marks. Repeated damage in the same area may point to burrs or rough surfaces on the tool.
With the right membrane mounting tool—and proper technique—you’ll gain more accurate, repeatable, and reliable triaxial test results. Whether you opt for manual precision or vacuum efficiency depends on your lab’s workflow, budget, and testing complexity.
-
Discover the key factors influencing triaxial test results to ensure reliable data in your soil mechanics projects. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand how a membrane mounting tool enhances test accuracy and repeatability in soil testing. ↩
-
Understanding the advantages of a smooth surface can enhance your tool selection for better performance. ↩
-
Exploring this design feature can help you choose tools that ensure consistent membrane alignment and stretching. ↩
-
Explore this link to learn effective techniques for preventing membrane tears, ensuring better results in your experiments. ↩
-
Discover methods to eliminate air trapped under membranes, which can enhance the accuracy of your experimental outcomes. ↩